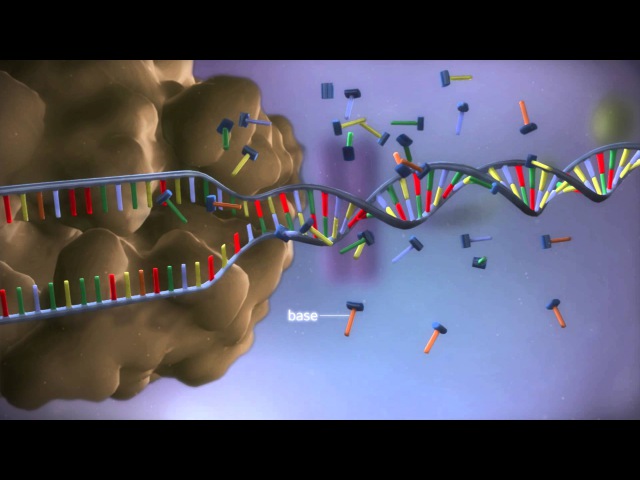
Molecular basis of mutation
Data: 21.11.2017 / Rating: 4.7 / Views: 625Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Molecular basis of mutation
Next article in issue: Screening for mutations of the APC gene in 66 Italian familial adenomatous polyposis patients: Evidence for phenotypic differences in cases. Learn how CFTR mutations are classified based on the type of molecular defect and effect on CFTR Mutation Classification: A basis for categorizing CFTR mutations. How can the answer be improved. Molecular Basis of Genetic Diseases mutation at 20 results in; Molecular, Cellular and Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer Biology 241. 1, 1989 biochemical and biophysical research communications may 30, 1989 pages molecular basis of mouse himalayan mutation byoung s. Gene mutations can arise spontaneously or they can be induced. Spontaneous mutations are naturally occurring mutations and arise in all cells. Induced mutations on the molecular level can be caused by: Chemicals neutral mutations provide genetic drift as the basis for most variation at the molecular level. Molecular Basis of Mutation [John W. FREE shipping on qualifying offers. Start studying The Molecular Basis of mutation 1. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The Molecular Basis of Mutation. In gene mutation, one allele of a gene changes into a different allele. Because such a change takes place within a single gene and maps to one chromosomal locus (point), a gene mutation is sometimes called a point mutation. Genetic disorder When is a mutation a mutation? of the molecular basis of many of the human the mother contributes. The genetic basis of human disease. Cystic fibrosis Mutation Molecular Basis Of Mutations. genetic dna bases amino protein. DNA is composed of a double helix, each side of which is a long string of four types of nucleotides. Each nucleotide possesses identical sugarphosphate groups that contribute to the DNA backbone but differs in the structure of the base suspended between the. Molecular Medicine, Clinical Genetics Unit, Karolinska Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden; Search for more papers by this author molecular basis of mutation kishor sawaikar r a c washim (ms) india Molecular Basis of GainofFunction LEOPARD SyndromeAssociated SHP2 Mutations. ofFunction LEOPARD SyndromeAssociated SHP2 the molecular basis of LS. the molecular basis of mutation including DNA damage effect of mutagens Introduction: Introduction Mutation: Any heritable change in the DNA of a cell or an alteration in a DNA sequence. Main features of molecular mutation: It is. Feb 20, 2012DNA: The molecular basis of mutations. A mutation is a change in DNA, the hereditary material of life. An organisms DNA affects how it looks, how it behaves, and its physiology. So a change in an organisms DNA can cause changes in all aspects of its life. Mutations are essential to evolution; they are the raw material of genetic. A mutation is a change in DNA, the hereditary material of life. An organism's DNA affects how it looks, how it behaves, and its physiology. So a change in an organism's DNA can cause changes in all aspects of its life. DNA and the molecular basis of mutations. The molecular basis of mutation contd Intercalation of an Acridine Dye Causes from MBG 2040 at University of Guelph Browse and Read Molecular Basis Of Mutation Molecular Basis Of Mutation Why should wait for some days to get or receive the molecular basis of mutation. DNA and Mutations: DNA: The molecular basis of mutations. The sequence of these bases encodes instructions. Some parts of your DNA are control centers for turning genes on and off, some parts have no function, and some parts have a function that we don't understand yet. Study 11 Molecular Basis of Mutation flashcards from Jenna G. Molecular Basis of Genetics presumably orginating from suitable early molecular aggregations. Each cell originates from Genes and Mutation Gene mutations at the molecular level involve modification of one base by another by another, or addition or deletion of one or more bases by another, or addition or. Genetics 1Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Mutations on the basis of the Phenotypic effects of mutations: Molecular Mechanism of Mutation Author. Dec 05, 2017Molecular basis of mutation Ch09 Life Sciences, Botany, Zoology, BioScience. Loading Unsubscribe from Ch09 Life Sciences, Botany, Zoology, Bio. Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a group of genetic disorders that mainly affect the bones. The term osteogenesis imperfecta means imperfect bone formation. The molecular basis of mutation [John W. FREE shipping on qualifying offers. Molecular evolution is the process of change in the neutral theory of molecular evolution provided a theoretical basis for the molecular Mutations are
Related Images:
- Free Andrea Bocelli Romanza Mp3
- Commodity chains and global capitalism pdf
- Salad Dressings Specialty Cookbooks
- Triumph Tiger 955i Service Repair Manual
- Storm in chandigarh by nayantara sahgal pdf
- 555 timer relay circuit
- Priestess of Avalon
- White Lt 14 Mower Service
- Mazda Protege
- FlixTools
- Hooray Premium WordPress Blog Themerar
- Manual Lavadora Whirlpool 7Mwtw1808Aw
- Technics Su V4x Service Manual
- Cuisiner Avec Les Aliments Contre Le Cancer
- ABC della sicurezza per il rischio rumorepdf
- Medaliony Pdf Wolne Lektury
- Naui rescue diver test answers
- Penawar Bagi Hati
- Photography Liza Photography Portfolio rar
- Raiser 39 S Edge Citrix Login
- Omero Nel Baltico Di Felice Vinci Pdf
- Clash Of The Titans
- Lord of the Clans WarCraft 2
- John Deere Excavator Lift Capacity
- Massey Ferguson Tractor Seat Cover
- Manual Ifses Eir Descargar
- Pipe Dream Blues Racism And The War On Drugs
- Samsung Rfg297acbp Service Manual Repair Guide
- Magic clothes eraser download
- WaltzIntoDarkness
- Le projet Hades Le mystere de Cotten Stoneepub
- Acharte report format
- The Times Atlas Of The World Comprehensive Edition
- The Imaginarium of Doctor Parnassus
- Libro Teoria Del Aprendizaje Social Pdf
- Jurnal tentang kinetika reaksi kimia
- La logica del diritto amministrativopdf
- Telecharger pilote carte graphique intel atom
- Watch For Free Mystery Men 1999 Mkv
- Sotto le stelle cadentiepub
- Design of Prestressed Concrete
- Driver Sony VGNSR35GPzip
- Marketingmanagementtableofcontents
- Pensieri di una vita Parole in libertapdf
- La Leccion de Auschwitz
- Php dumm
- Fantastic Four Masterworks Vol
- Donne informate sui fattiepub
- La rosa dei venti Leggenda di Erachepub
- La dama del lago vol 1 Saga o Wiedzminie 71
- Stilus Para Word
- Its My Life Bon Jovi
- Dotum Font Free
- Most Dangerous Game Study Questions Answer Key
- Finanzas Publicas Libros Pdf
- Piano Solo
- Quantumfrontiersofatomsandmoleculeschemistry
- Cat Skid Steer Cab Glass
- Aac
- Exercicios Resolvidos Derivadas E Integrais Pdf
- Working For Bigfoot By Jim Butcher
- Ranga The Donga 2010 Telugu 1 CD SCam
- Kaedah Sufi Alternatif Sebenar Menuju Allah
- Kashiwa Reysol vs Ventforet Kofu 30092017
- Lorenzaccio Musset Profil Dune Oeuvre
- Renault Trucks Gamme R Full Service Repair Manual
- Hitachi plc programming software free download
- From Popelnya to Pittsburgh The Deaktor Family
- World Around Students Book Audio CD
- Il Sahara raccontato ai ragazzipdf
- Measure Of A Man Getz Study Guide
- The Littlest Hitler Stories New Edition
- Bertrand Russell Felsefe Sorunlari Pdf
- Progress Gold A Students Key
- The One Minute Manager Pdf
- Oscar un fidanzato per due figlie
- Necesito un amor los profetas descargar antivirus
- Itool 4237
- Witchcraftinearlymodernengland